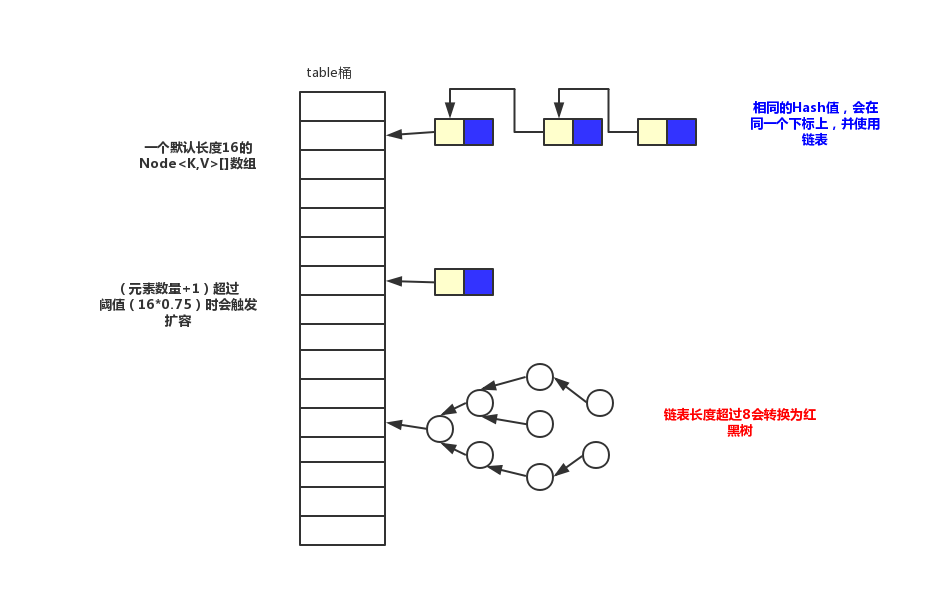
画了一张结构图,欢迎指正。
变量
1 | /** |
构造方法
1 | /** |
无参的构造方法
这个应该就是我们最常用的构造方法,将负载系数初始化为默认的系数。
声明容量的构造方法
调用了声明容量和负载系数的构造方法
声明容量和负载系数的构造方法
首先会判断这个容量是否符合要求,并且最大值是
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY=1<<30,从这里可以看出map的最大容量值。然后再计算threshold值,这个值表示扩容的阈值,当键值对的数量超过这个值就会扩容。下面会介绍一下tableSizeFor()方法。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}这个方法的主要作用是找到等于或大于cap的,最小的2的幂。比如我们传入
6,他返回8,传入8,返回8。利用了位运算。参数为map的构造方法
负载系数使用默认的系数,然后将传入的map参数放到新的map中。这个
putMapEntries()方法在下面的putAll方法中进行解读。
从这里可以看出,在构造函数里面并没有对存储键值对的变量进行初始化,这个初始化过程是放在第一次放的过程中。
插入 put(K key,V value)
1 | public V put(K key, V value) { |
计算hash
在放的时候用到了hash()方法对键做哈希运算,并且没有直接运用Object的hashCode()方法,在这个的基础上又进行了一些运算。这个16位也是有原因的,具体后面再过来讲。
1 | static final int hash(Object key) { |
扩容
还用到了扩容的方法
1 | final Node<K,V>[] resize() { |
putAll
1 | public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { |
get
给出key,获取value。
1 | public V get(Object key) { |
remove()
根据key删除值。
1 | public V remove(Object key) { |
containsKey(Object key)
判断map中是否包含这个key
1 | public boolean containsKey(Object key) { |
从代码可以看出,他其实先调用了根据key查询的方法,然后判断这个key对应的键值对是否存在,getNode方法也在上面有用到。
containsValue(Object value)
根据value判断是否存在这个map中。
1 | public boolean containsValue(Object value) { |
keySet()
1 | public Set<K> keySet() { |
values
1 | public Collection<V> values() { |
entrySet
1 | public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { |
treeifyBin
1 | final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { |
总结
- 扩容机制为2倍扩容,最大容量为2的30次幂,并且扩容是放到这一次的结束进行判断下一次是否需要扩容,而不是放到下一次的开始。
- 实现为数组+链表+红黑树(jdk1.8之后)
HashMap是无序的,因为放值的时候下标是(n - 1) & hash计算出来的,如果hash值相同则为同一个下标,然后使用链表或树结构。比如我现在顺序放三个key,(a,b,c)。如果a和c的hash值是一样的,b跟他俩不一样,那么最终得到的结果就是a和c是一起拿出来的。他们中间不会有b。如果希望有序需要使用LinkedHashMap。